Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Sale conditions
Sale conditions of wood are specified by the regulation of Director – General of the Sate Forests.
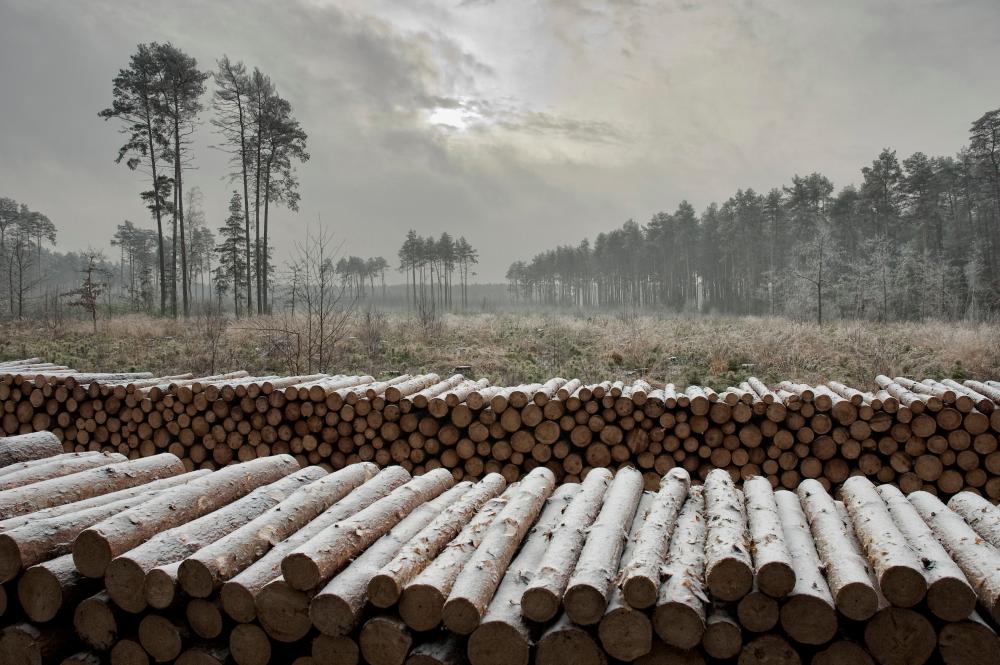
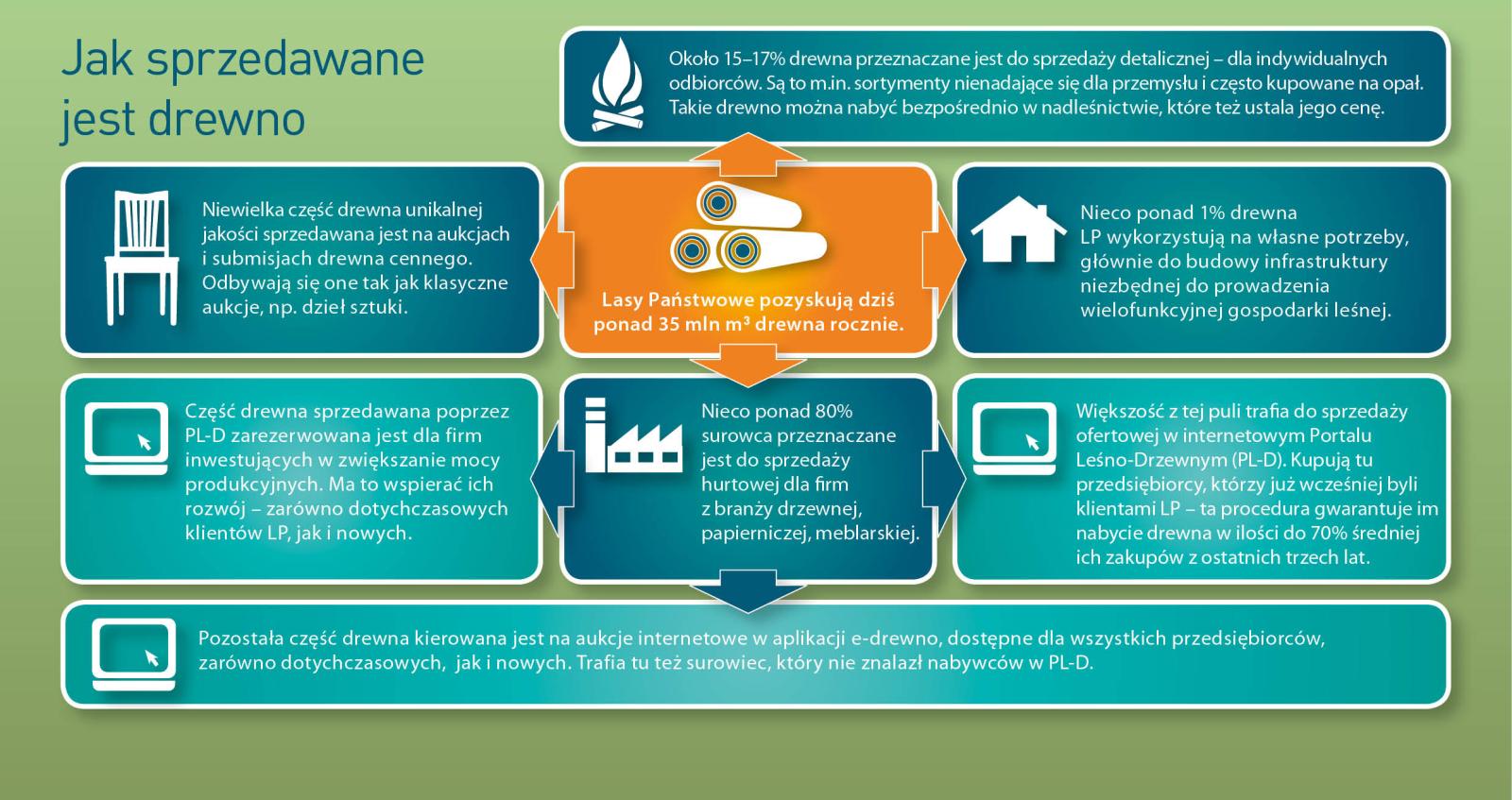
Within the framework of the individual sale , the foresters try to meet the fast growing demand, because more and more people use wood in order to heat their houses. Contrary to general opinion, these are not only village people, even though they prevail among recipients. The growth of firewood demand is the result of occurrence of new housing estates built in the suburbs of large agglomerations, where houses are usually equipped in fireplace heating installations.
Firewood is not only the most ecological heat source, but also is much more attractive in respect of relation of price and electric efficiency, rather than cola, oil, gas or electric power.
In recent years, the Sate Forests increased the sale of firewood of one third – up to over 4 million cubic meters annually. Firewood is not only the most ecological heat source, but also is much more attractive in respect of relation of price and electric efficiency, rather than cola, oil, gas or electric power. Some of customers choose already prepared and cut into pieces wood, the others very willingly obtain it by themselves after arranging all details and fulfilling particular safety conditions, and after paying the fee; that concerns mainly so called "thinnings". Such a raw material is very cheap, that is why many people from village areas profit from such possibility.
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Lasy Nadleśnictwa
Lasy Nadleśnictwa
 Nasze lasy (Fot. Adrian Pietrzak)
Nasze lasy (Fot. Adrian Pietrzak)
 Nasze lasy (Fot. Adrian Pietrzak)
Nasze lasy (Fot. Adrian Pietrzak)
 Nasze lasy (Fot. Adrian Pietrzak)
Nasze lasy (Fot. Adrian Pietrzak)
 Nasze lasy z lotu ptaka (Fot. Adrian Pietrzak)
Nasze lasy z lotu ptaka (Fot. Adrian Pietrzak)
 Nasze lasy z lotu ptaka (Fot. Adrian Pietrzak)
Nasze lasy z lotu ptaka (Fot. Adrian Pietrzak)
 Nasze lasy z lotu ptaka (Fot. Adrian Pietrzak)
Nasze lasy z lotu ptaka (Fot. Adrian Pietrzak)
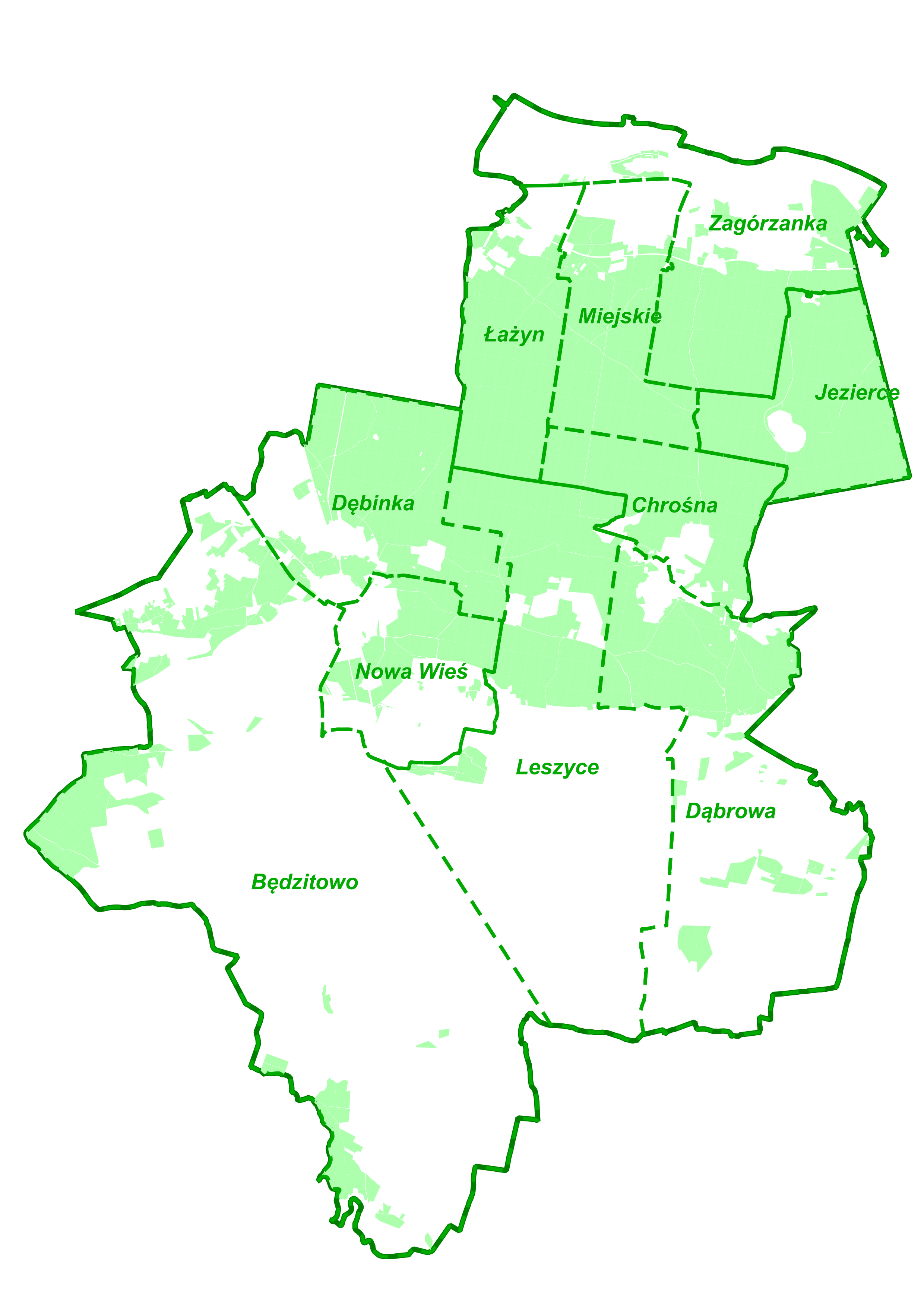
Pod zarządem Nadleśnictwa Solec Kujawski znajduje się niemal 15 tys. ha lasów. Tutejsi leśnicy opiekują się także 450 ha lasów prywatnych.
Rzeźba terenu nadleśnictwa uformowała się w następstwie erozyjnej działalności wód roztopowych płynących od moren czołowych fazy pomorskiej i wód rzecznych pochodzących z południa. Dużą formę erozyjną Kotliny Torunskiej tworzy 11 poziomów terasowych zarówno erozyjnych, jak i erozyjno-akumulacyjnych. Piaszczyste terasy były bardzo podatne na działalność wiatru w okresie późnego glacjału i na począku holocenu, w zwiazku z czym na większości poziomów terasowych rozwinęły się wydmy i pola piasków przewianych. Dominują tu wydmy paraboliczne i wałowe osiągające nawet 30 m wysokości względnej, na zapleczu których występują niecki deflacyjne z warstwami torfu lub murszu.